Related Blogs
- Finance Ops Transformation in GBS - Balancing Technology, Talent, and Data-Driven Insights for Peak Performance
- Improving Customer Experience: What Leaders Say Works Best
- Unlocking the Future of Procurement: Balancing Cost, Automation, and Strategic Relationships for Maximum Value
- Driving the Gen AI Revolution
- THE ESG CONUNDRUM: Why High Costs and Data Complexities are Stalling Progress and How Capability Centers can Turn the Tide
- BUSINESS AS USUAL IS OVER: Sustainability Disruptions will Redefine the Future of Business
Contact Us
-
Call Us:
+91-11-26674814
-
Mail Us
contact@quintesglobal.com
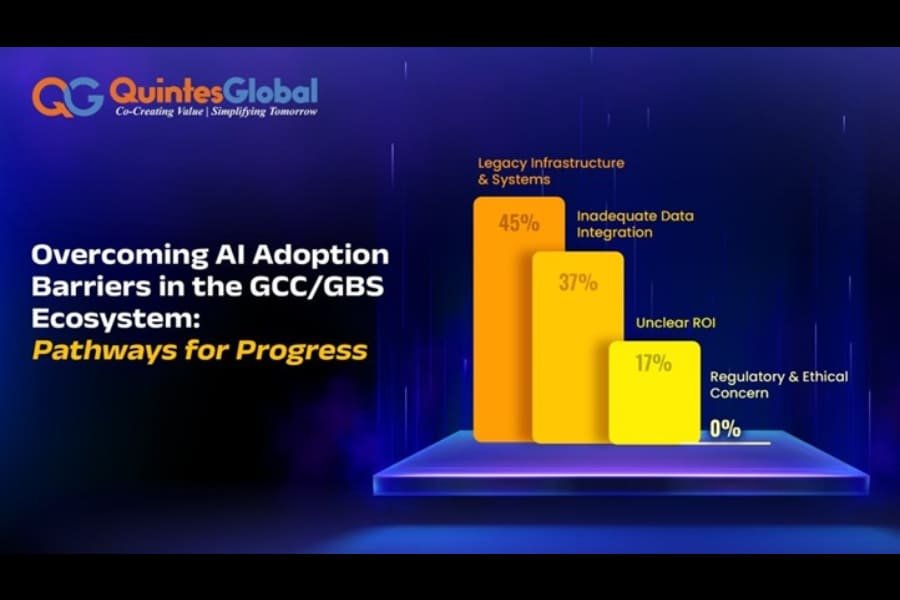
Overcoming AI Adoption Barriers in the Gcc Gbs Ecosystem Pathways for Progress
Introduction
1. Legacy Infrastructure & Systems: Modernizing the Foundation for AI
The dominance of legacy systems as the leading obstacle (45%) is not a surprise. Many GCCs and GBS centers have extensive pre-existing technology stacks, often built on outdated infrastructures. These systems can be challenging to modernize due to high operational risks, integration complexities, and prohibitive costs.
Impact on AI Adoption
Legacy systems typically lack the scalability, flexibility, and real-time data processing capabilities required for AI applications. When systems are not designed to handle large datasets or enable seamless integration with modern tools, AI implementation can lead to inconsistent outcomes, longer deployment times, and resource inefficiencies.
Typical strategies adopted to overcome legacy system challenges
- Adopt a Phased Modernization Approach: Rather than a complete overhaul, organizations can opt for incremental modernization. By prioritizing critical systems and integrating cloud-based solutions where feasible, companies can enhance compatibility with AI tools gradually.
- Leverage Middleware Solutions: Middleware can act as a bridge between legacy systems and modern AI applications, enabling data exchange without disrupting core processes.
Case Example: A global financial services GCC, embarked on a phased modernization journey by integrating a cloud-based AI platform to analyze customer data, bypassing its legacy CRM system. This allowed the company to leverage AI for customer insights without compromising existing systems.
2. Inadequate Data Integration: Building a Unified Data Ecosystem
Inadequate data integration (37%) ranks second, reflecting the challenges of managing, harmonizing, and structuring large datasets. Data is the lifeblood of AI; without a cohesive data integration strategy, organizations cannot harness the full potential of AI algorithms.
Impact on AI Adoption
Disconnected data systems lead to data silos, making it challenging for AI models to access and process complete, accurate, and timely information. This results in lower AI performance and diminishes trust in AI-based insights, as stakeholders are unsure of the data’s reliability.
Typical Strategies that have helped GCCs to improve data integration
- Implement a Centralized Data Management Platform: A centralized data repository, such as a data lake or warehouse, can consolidate information from different systems, breaking down data silos and enabling real-time data access.
- Use Data Integration Tools and APIs: Automated data integration tools and APIs facilitate seamless data transfer across systems, allowing AI models to access diverse datasets for more accurate insights.
Case Example: A leading consumer goods company faced data integration challenges due to fragmented systems across regions. By deploying a centralized data lake and leveraging APIs to integrate data from disparate systems, the company was able to deploy AI-driven demand forecasting models, significantly reducing stockouts and improving supply chain efficiency.
3. Unclear ROI: Making the Business Case for AI Investments
Another 17% of respondents indicated unclear ROI as a significant barrier. Many organizations are hesitant to invest in AI without a clear, measurable return on investment, especially given the costs associated with development, deployment, and ongoing maintenance.
Impact on AI Adoption
When AI initiatives lack quantifiable benefits, stakeholders may view them as experimental rather than strategic. Unclear ROI often stems from a lack of understanding of AI’s potential impact on specific business functions, leading to missed opportunities and limited budget allocation.
Commonly deployed strategies that demonstrate AI ROI
- Identify and Target High-Impact Use Cases: Business process consultants can help clients focus on AI applications that deliver quick wins with measurable outcomes, such as automation in repetitive tasks or predictive maintenance in operations.
- Pilot Programs with Measurable Metrics: Running small-scale AI pilot projects with defined KPIs can showcase quick wins and prove value, fostering buy-in for further investment.
Case Example: An insurance GCC piloted an AI-driven claims processing tool targeting 20% of its operations, demonstrating a 30% reduction in processing time. The pilot’s success helped secure funding for expanding AI across other functions.
Regulatory & Ethical Concerns: Why they are not a major barrier (Yet)
Interestingly, none of the poll respondents selected Regulatory & Ethical Concerns as a barrier to AI adoption. This might suggest that, for now, GCCs and GBS organizations are more focused on overcoming operational and infrastructure-related challenges. However, as AI adoption scales up, regulatory and ethical considerations could become a more prominent issue.
For many organizations, regulatory and ethical issues—such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and compliance—may not yet be perceived as immediate roadblocks, when it comes to AI adoption. This can be due to:
- Early Stages of AI Adoption: Many GCCs/GBS centers are still in the early stages of AI implementation, focusing on pilot projects or limited applications rather than large-scale deployments that might trigger regulatory concerns.
- Established Compliance Standards: Organizations in heavily regulated industries (like finance and healthcare) often have established compliance frameworks that support data handling and governance, making it easier to align AI with existing regulatory requirements.
- Focus on Internal Processes: When AI is applied primarily to internal processes, like automation or predictive analytics, the ethical concerns associated with customer-facing AI (e.g., bias in customer algorithms) may not be as pressing.
Looking Ahead: Navigating the Future of AI in GCC/GBS
The path to widespread AI adoption in the GCC/GBS ecosystem is complex but achievable. By addressing legacy infrastructure, enhancing data integration, and building a strong business case for AI, organizations can unlock the technology’s transformative power. Business process consultants play a crucial role in guiding companies through these transitions, helping them harness AI’s potential to drive meaningful change.
As AI matures and more GCCs begin to use it in ways that directly impact decision-making or customer-facing processes, regulatory and ethical challenges are most likely to come into sharper focus. BPM experts will then need to help clients implement ethical AI frameworks and ensure compliance with evolving global AI regulations. Preparing for this now—by fostering a strong ethical foundation and building transparent, explainable AI models—can give organizations a competitive advantage in the long term.
To conclude, as GCCs and GBS centers strive to remain competitive and resilient, overcoming these obstacles will be essential in shaping the future of enterprise services.